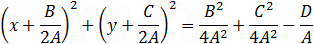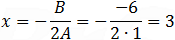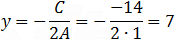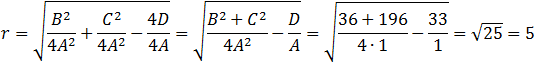Circle defined by 3 points calculator
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Equation of a circle passing through 3 points (x1, y1) (x2, y2) and (x3, y3) summary

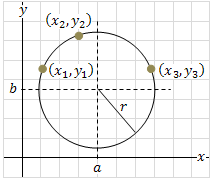 |
|
||||
|
The coefficients A, B, C and D can be found by solving the following determinants: 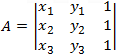 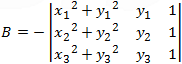 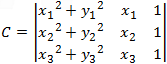 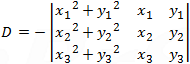 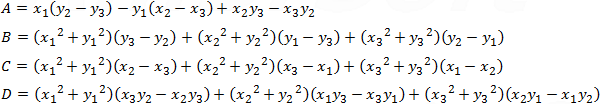 |
|||||
|
Center point (x, y) and the radius of a circle passing through 3 points (x1, y1) (x2, y2) and (x3, y3) are: 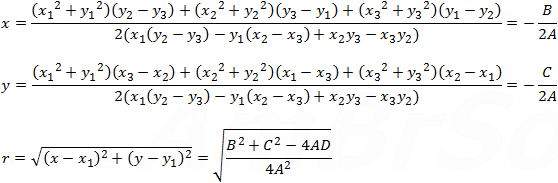 |
|||||
Example 1 - Circle Defined by 3 Points

|
|||||||||
|
Find the equation of a circle that passes through the points (⎯3 , 4) , (4 , 5) and (1 , ⎯4).
|
|||||||||
|
|||||||||
Example 2 - Circle Defined by 3 Points

|
Find the equation of a circle and its center and radius if the circle passes through the points (3 , 2) ,
(6 , 3) and (0 , 3). |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
After dividing all terms by 6 we get: A = 1 B =−6 C = −14 D = 33.
And the equation of the circle is: x2 + y2 ⎯ 6x ⎯ 14y + 33 = 0 In order to find the radius of the circle use the general circle equation and perform some basic algebraic steps and with the help of the square form (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2 we get
The last equation is a circle with the center and radius equals to (notice the minus sign at x and y):
The equation of the circle can be presented by the center and the radius as: (x ⎯ 3)2 + (y ⎯ 7)2 = 52
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

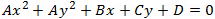
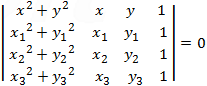
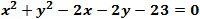
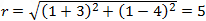
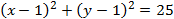
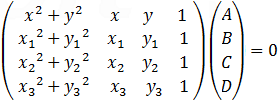
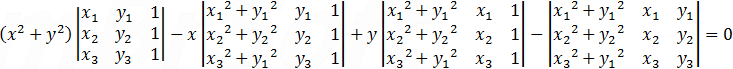




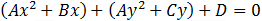
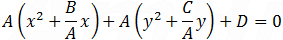
![A[(x+B/2A)^2-B^2/(4A^2 )]+A[(y+C/2A)^2-C^2/(4A^2 )]+D=0](/TrigoCalc/Images/Circle/eq2h.png)
![[(x+B/2A)^2-B^2/(4A^2 )]+[(y+C/2A)^2-C^2/(4A^2 )]=-D/A](/TrigoCalc/Images/Circle/eq2i.png)