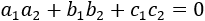3D lines summary
|
Distance between two 3D points: (x0 , y0 , z0) and (x1 , y1 , z1) |
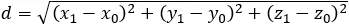
|
|
Line passing through two points (x0 , y0 , z0) and (x1 , y1 , z1) 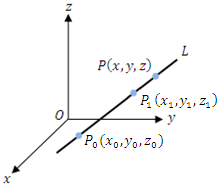
|
A point P(x, y, z) is on the line L if and only if the direction numbers determined by P0 and P1 are proportional
to those determined by P1 and P2. If the proportionality constant is t we see that the conditions are: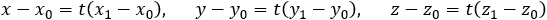 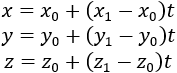 (1)
|
The parametric equations of line L through the point with direction numbers a, b and c are given by the equations:
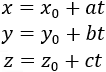 (2)
|
|
Two points formed by the equation of a line also may be written symmetrically as:
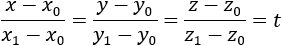 |
|
|
Two lines with slopes (a1, b1, c1) and (a2, b2, c2)
are perpendicular to each other if and only if: Two lines are parallel if:
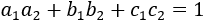 |
Direction angles, direction cosines and direction numbers

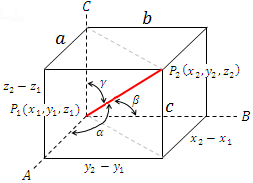
A line presented by a vector, produces angles respective to the x, y and z axis, these angles are known as direction angles and are presented by the letters α, β and γ
If the projection of the line presented by a vector as L: xi + yj + zk (i, j and k are denoting the vector directions in x, y and z direction). The magnitude of the line is also known as modulus of the vector is:
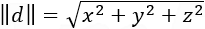
According to the vector calculus the division of the projection length on each axis divided by the magnitude of the vector produces the cosine of the angle from the vector to the axis.
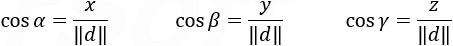
These values of the angles are known as the directional cosines.
Notice that the sum of the squares of the directional cosines is equal to 1:
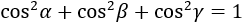
Presentation of 3D lines

A 3D line can be presented by several methods, the most frequent way is by parametric equations or by the classical form, another way is by vector notations, the line can also be presented by defining two points along the line.
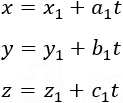
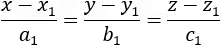
The parametric and the classic presentation of the line are actually the same, to show this we take the values of the division of x, y and z as equal to t:
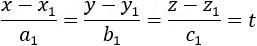
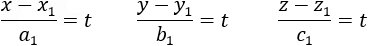
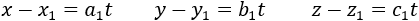
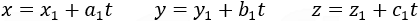
And we receive again the parametric equations of the line, different values of t describes different points along the line.
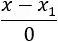
This is incorrect mathematically, but in the line notation it means that x = x1 and the line; is located on a plane parallel to the y-z axis.
If two direction numbers, let say a1 = b1 = 0 , the line is parallel to the z axis. All 3 direction numbers can not be 0 as there will be no line but only a point.
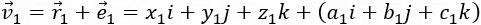
Notice that r1 is a location of a point on the line and e1 (in the parenthesis) defines the direction numbers of the line.
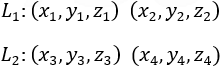
This method includes choosing one point on the line, let say (x1, y1, z1) and then calculating the direction numbers a1, b1 and c1 of the line L1:
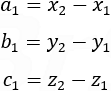
3D lines - Example 1

a) from equation (1) we obtain the parametric line equations: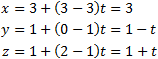 b) distance from any point (x, y, z) to the point (3, 1, 1) is: 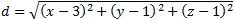 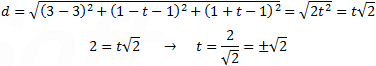 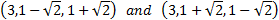 |
3D lines - Example 2

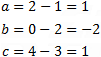
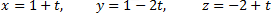
3D lines - Example 3

The length of the line is the distance between the two 3D points:
![d=√((3-0)^2+[8-(-4)]^2+(6-0)^2 )=√189=13.75](/TrigoCalc/Line3D/Eq/eq4j.png)
To find the cosine of the angles between the line and the axis, we divide each axis length with the total length of the line d.
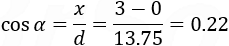
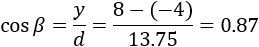
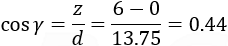
Checking that the sum of the cosines square is equal to 1.
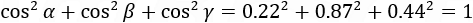
3D lines - Example 4

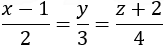
Find the equation of the line that passes through the point P (5, −1, 4) and is perpendicular to the given line.
x = 1 + 2t y = 3t z = −2 + 4t
The vector QP streched from the line to the point P is:
QP = (1 + 2t − 5)i + (3t − (−1))j +(−2 + 4t − 4)
QP = (−4 + 2t)i + (1 + 3t)j + (−6 + 4t)k
The line vector is: vL = 2i + 3j + 4k
To find the intersection point of the line with the perpendicular line we use the fact that the dot product of the vectors is equal to 0, QP ∙ vL = 0
[(−4 + 2t)i + (1 + 3t)j + (−6 + 4t)k] ∙ (2i + 3j + 4k) = 0
−8 + 4t + 3 + 9t −24 + 16t = 0
4t + 9t + 16t = 24 − 3 + 8
29t = 29
t = 1
And the intersection point from the parametric line equations is: x1: (3, 3, 2)
From the intersection and the given points x0: (5 , −1 , 4), we can derive the equation of the perpendicular line:
x = x0 + (x1 − x0)t = 5 + (3 − 5)t = 5 −2t
y = y0 + (y1 − y0)t = −1 + (3 + 1)t = −1 + 4t
z = z0 + (z1 − z0)t = 4 + (2 − 4)t = 4 − 2t
The direction numbers of the perpendicular line are (−2 , 4 , −2)
From the condition for two lines to be perpendicular we have:
−2 * 2 + 4 * 3 + −2 * 4 = 0