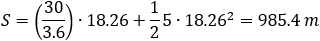The acceleration describes the constant amount of increase or decrease in the speed of an object along the travel path. There are cases that the acceleration is not constant but depends on time. a = a(t) The value of speed is a scalar value which has only pure values compared to the velocity that has values and direction in space.
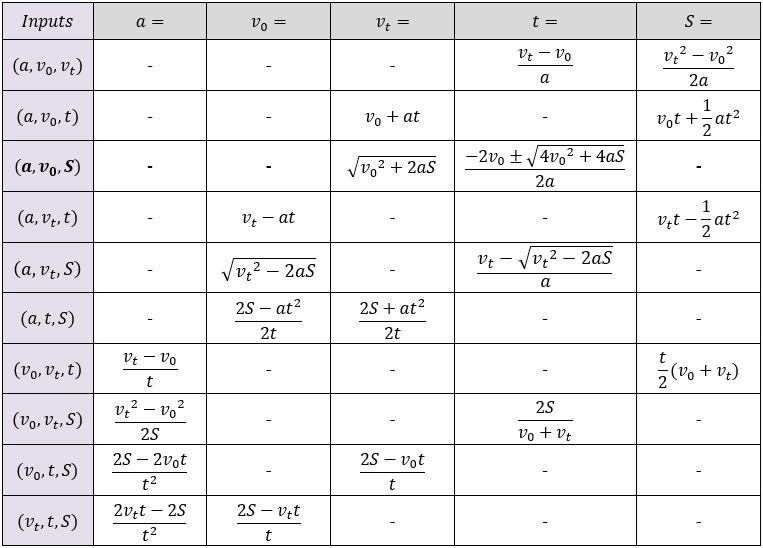
Acceleration equations as a function of different inputs
Car racing simulation


Racing cars example
A car and a motorcycle are racing in a racetrack of a length of 1km if the car starts with an initial velocity of 30 km/h and an acceleration of 5 m/s2 and the motorcycle stars from rest with an acceleration of 6 m/s2. Which one of them will win the race.
Solution - The winner of the race will be the one that will pass the complete length of the racetrack in the lowest time, so for each of the competitors we shell find the total time to complete the whole track, we use the equation as follows:
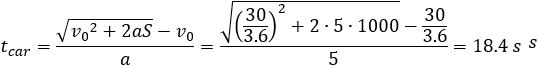
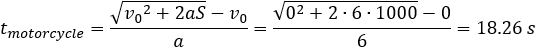
The time of the motorcycle to finish the track is less then the car hence the motorcycle wines the race. The initial velocity is divided by 3.6 to change velocity units from km/h to m/s.